Fewer Virus Curbs Help India Manage War-Induced Price Pressures
A slew of data from services activity to bank credit pointed to the return of demand last month.

(Bloomberg) -- India’s economic activity held steady in March as the lifting of most virus containment measures boosted demand, keeping war-induced price pressures from dampening the recovery for now.
A slew of data from services activity to bank credit pointed to the return of demand last month. The needle on a dial measuring so-called ‘Animal Spirits,’ however, remained at 5 as the gauge uses the three-month weighted average reading to smooth out volatility in the single-month numbers.
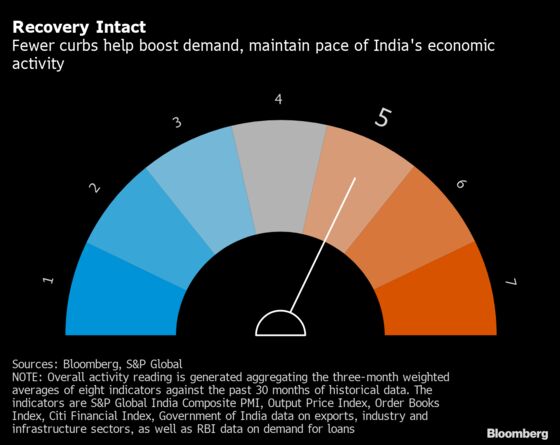
The stronger sentiment may give way to uncertainty as Russia’s war-induced supply disruptions further impact global commodities, driving up prices and possibly crimping demand. Also, a resurgence in virus cases, for now mostly limited to the capital New Delhi, revives the possibility of fresh activity curbs barely a month after they were dismantled.
Below are details of the dashboard. (For an alternative gauge of growth trends, follow Bloomberg Economics’ monthly GDP tracker -- a weighted index of 11 indicators.)
Business Activity
Purchasing managers surveys showed activity at Indian service providers grew at the strongest rate since December, while factories signaled expansion. That helped push the S&P Global India Composite PMI Output Index to its strongest this year at 54.3, above the 50 threshold that divides growth and contraction.
Output prices rose in March as goods producers and service providers passed on higher input costs to clients, with the composite output index rising at the fastest pace since November.
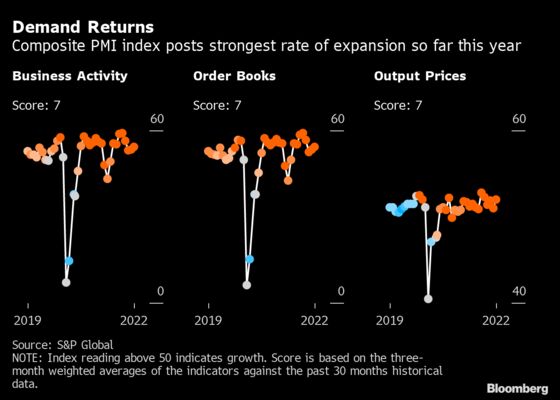
“Looking ahead, input costs are likely to rise at faster rate with domestic oil firms starting to bring fuel prices into line with higher global prices,” Bloomberg Economics’s Abhishek Gupta wrote in a report. “This should apply another drag on growth.”
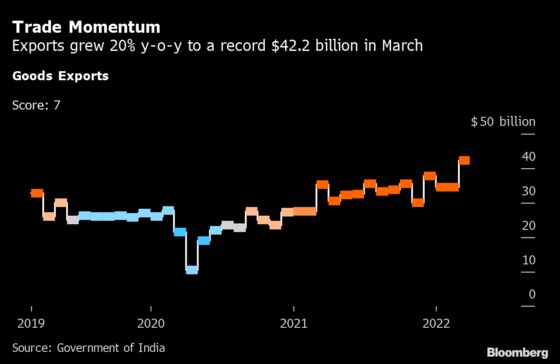
Exports
Exports raked in $42.2 billion in March, the highest by value in data going back to 2002, led by demand for petroleum products and engineering goods. That helped narrow the trade deficit to $18.5 billion from $20.9 billion in February.
Consumer Activity
The slack in the automobile sector continued with passenger vehicle sales falling for a seventh straight month, declining 4% in March from a year ago. The decline isn’t a demand-side phenomenon as much as it is a supply-side one, with carmakers grappling with chip shortages and increasing input costs.
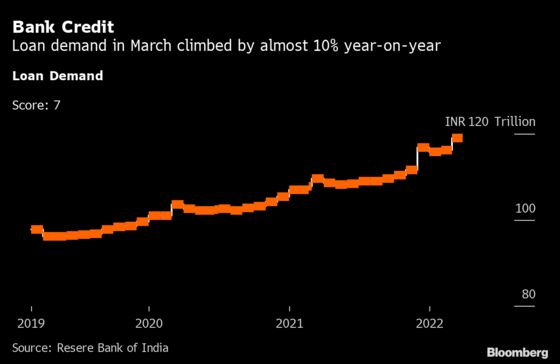
Other indicators of consumer activity were encouraging, with bank credit growth at 9.6% in end-March, from 7.9% the previous month. Liquidity conditions continued to remain in surplus.
Industrial Activity
Factory output growth picked up, rising 1.7% in February, aided by mining and electricity output. Output at eight infrastructure industries, which make up 40% of the industrial production index, grew 5.8% in February from 4% the previous month. Both reports are published with a one-month lag.
©2022 Bloomberg L.P.